

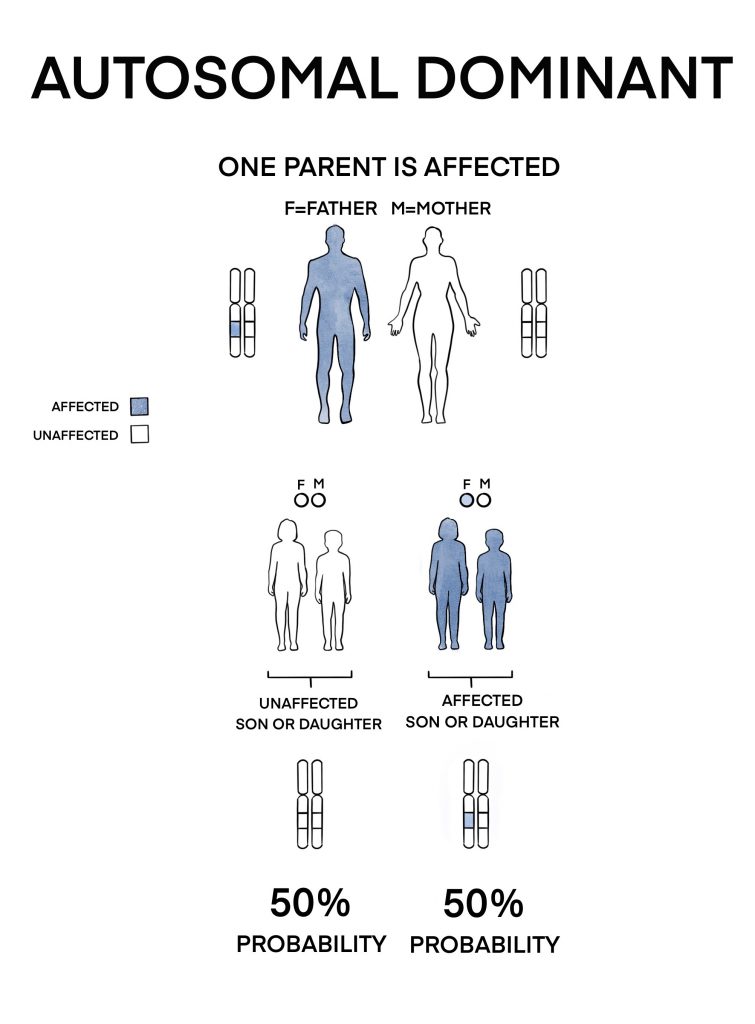
A child has a 50% probability of inheriting the mutant gene. Each affected person typically contains a single parent who is also affected. To be afflicted by an autosomal dominant inheritance, a person just needs one mutant copy of the gene. For instance, achondroplasia, the most prevalent form of dwarfism, is commonly thought to be a dominant illness, however, children with two achondroplasia genes do have serious and generally fatal bone conditions, which achondroplasics could have been carriers for. Even though distinctions between autosomal and X-linked kinds are clear, the distinctions between recessive and dominant types are not "hard and fast". However, genomic imprinting and uniparental disomy might have had an impact on inheritance patterns. Single-gene diseases could be passed down the generations in a variety of ways. The outcome of a single mutated gene is a single-gene disorder (or monogenic condition). Because of the large variety of genetic abnormalities, roughly one in every twenty-one people is affected by a "rare" genetic disorder. As a consequence of congenital genetic mutations, approximately 65 percent of people experience some sort of health issue. A known single-gene problem affects about 1 in 50 persons, whereas a chromosomal issue affects about 1 in 263 people. There are around 600 ailments that can be treated. There are about 6,000 documented genetic illnesses, and new genetic abnormalities are documented in the medical literature on a regular basis. Only a small percentage of diseases are inherited from the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA. Certain illnesses have X-linked inheritance and are associated with mutations on the X chromosome. It is sometimes referred to as a hereditary disease whenever the genetic abnormality is inherited through one or both parents. The mutation that causes the disorder can happen suddenly before embryonic development (a de novo mutation), or it could be acquired from two parents who've been carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance), or through a parent who already has the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). Although polygenic illnesses are the most frequent, the term is typically applied to conditions that have a single genetic origin, such as a mutation in a gene or chromosome. A chromosomal anomaly or a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) could be the reason for the same. Eso you actually need both? Wow, a wheels to be mutated in orderto actually express the show the diseased finito.Genetic Disease:- A genetic disorder is a medical condition caused by one or even more genetic defects. But since they do have one copy of the, uh, of the correct O'Neil, they are actually eventually able to regulate, um uh, I on and on DDE What? Er e flux from the cells properly. Um, and for individuals that air only missing one copy of this gene, they may produce certain defective, uh, channels that would not enable, uh, I arms to be regulated properly. Uh, cftr gene encodes a protein for that serves as a chloride, um on and and a chloride channel that helps ions get into and out of the cell. Um, and this type of inheritance pattern makes a lot of sense when we think more about what the protein itself does. And, uh, the oh correct explanation of the pattern hair it's is that it is, um, be autism will recess it. So from that we know that it is unlikely to be, Ah, a dominant trait. Neither parent has any sign of the disease.
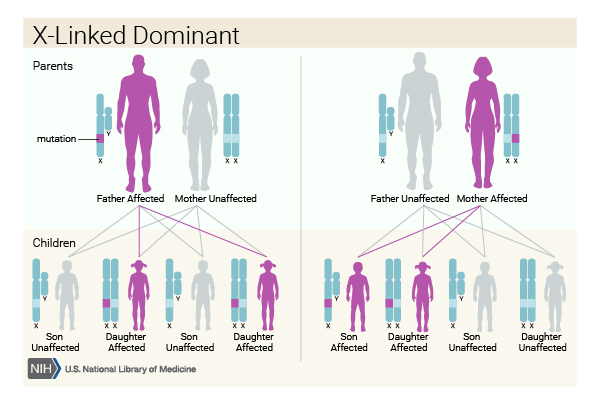
Uh, the other thing, uh, that's notable about cystic fibrosis inheritance is that it can affect, uh, children, even though the parents I have no both parent. It affects males and females, similarly, s o From now we can begin to deduce that it's unlikely to be excellent, excellent or sex linked. So, uh, when we think about cystic fibrosis, the inheritance patterns, one of the things we need to keep in mind is that it is set. Trans membrane conducted its regulator, Jean CFTR. So, uh, cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene for, uh, which stands for the cystic fibrosis.
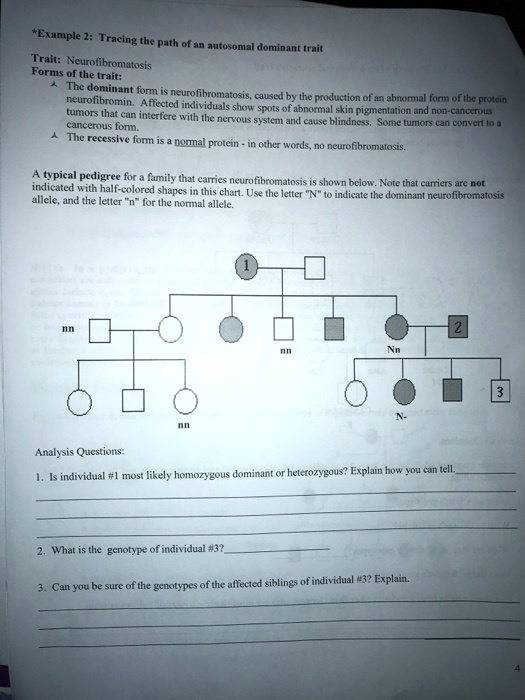
So this question is discussing the inheritance of cystic fibrosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
